Space is no longer just about exploration. It is transforming industries, reshaping economies, and driving technological progress. From powering smart devices to improving supply chains, space-enabled technologies are now part of daily life. As costs decrease and access improves, the impact of space is reaching beyond aerospace, influencing industries like retail, agriculture, and disaster response.
The Expanding Space Economy: Growth, Innovation, and Industry Transformation
The global space economy is experiencing unprecedented growth. It was valued at $630 billion in 2023 and is projected to reach $1.8 trillion by 2035, according to the World Economic Forum and McKinsey & Company. The expansion is driven by satellite communications, Earth observation, and positioning technologies, which support essential services such as GPS navigation, climate monitoring, and global connectivity.
Satellite launches have increased by 50 percent annually over the past two decades. At the same time, launch costs have dropped significantly, making space more accessible and attracting record investment. In 2021 and 2022 alone, over $70 billion was invested in space-related ventures, underscoring the long-term economic potential of the sector.
The space economy will continue to grow and will generate attractive returns for investors with the insight to identify promising sub-sectors and the patience to wait out the postSPAC [special purpose acquisition company]12 hangover. In addition to rewarding investors, the space economy will help us solve the world’s major problems.
Matt O’Connell, Operating Partner, DCVC for World Economic Forum and McKinsey & Company
Beyond traditional aerospace, space is becoming a major economic force. By 2035, more than 60% of space-driven revenue is expected to come from industries such as logistics, retail, and digital communications. Satellite tracking improves supply chain efficiency, while sectors like agriculture and food distribution leverage space-based data for better resource management.
Space access’s falling costs drive innovation, making satellite-powered applications viable across various sectors. Advances in mega-rocket technology enable larger payloads and more ambitious missions, while space tourism is emerging as a new market, projected to reach $4 to $6 billion by 2035, primarily driven by in-orbit stays for ultra-high-net-worth individuals. With rising investment and technological advancements, the space industry is positioned to reshape economies and redefine industries in the coming decades.
The Role of Space Companies
A wide range of companies contribute to the expansion of the space industry. Each plays a role in advancing technology, infrastructure, and exploration.
- Launch Providers focus on developing reusable rockets to reduce launch costs and enable frequent missions. Companies such as SpaceX, Rocket Lab, and Blue Origin are leading this segment.
- Satellite Manufacturers produce satellites used for communication, Earth observation, and defense applications. Boeing, Lockheed Martin, and Airbus are key players in this field.
- Ground Infrastructure and Operations organisations build and maintain satellite control stations, data processing centers, and global connectivity networks.
- Orbital Services and Space Tourism businesses such as Axiom Space and Virgin Galactic are developing in-orbit services, including private space stations and commercial space travel.
- Deep-space exploration and Colonisation ventures are working to expand human presence beyond Earth, with missions to the Moon, Mars, and other celestial bodies.
The Expanding Influence of Space Technology Across Industries
Space technology is transforming multiple industries and enabling new business models.
- Supply Chain and Transportation companies use satellite tracking for fleet management, route optimisation, and global supply chain visibility.
- Food and Beverage companies benefit from positioning and navigation technology, which enhances last-mile delivery for services such as UberEats and DoorDash.
- Retail and Consumer Electronics businesses rely on satellite broadband for e-commerce expansion. Wearable devices powered by space-based navigation are changing personal fitness tracking.
- Defense and Security investments in military space assets are growing. Applications include intelligence gathering, surveillance, and secure communications.
- Healthcare and Life Sciences depend on satellite communications for telemedicine and remote health monitoring, improving access to healthcare in underserved regions.
Key Trends Driving Growth
Several trends are shaping the future of space and accelerating its influence across industries.
Mega Rocket Launches and Cost Reduction
Companies such as SpaceX, Blue Origin, and Relativity Space are developing next-generation launch vehicles. The decline in launch costs has made frequent space missions more feasible and increased accessibility for commercial ventures.
Satellite Proliferation and Data Expansion
The number of satellites launched each year has grown exceptionally, with thousands more expected to enter orbit in the coming years. Companies such as Starlink, OneWeb, and Amazon’s Project Kuiper are expanding satellite constellations to improve global connectivity. Demand for space-based communication, navigation, and Earth observation services is rising, benefiting the logistics, digital communication, and climate monitoring industries.
Integration of Space Data into Daily Life
Space-based services now influence industries beyond aerospace. Satellite broadband is closing connectivity gaps in remote areas. GPS advancements are supporting autonomous vehicles and smart logistics. McKinsey predicts that more than half of new commercial applications will rely on space-based data and infrastructure in the next decade.
Investment from Governments and the Private Sector
Governments in the United States, China, India, and Japan continue to fund defense, research, and public infrastructure projects. Private investment in space reached an all-time high in 2021 and 2022, with over $70 billion flowing into the sector. This capital fuels innovation in space tourism, in-orbit services, and commercial space stations. Space mining, lunar exploration, and deep-space missions are also emerging as areas of interest.
Challenges and Considerations
As the space industry expands, several challenges must be addressed to ensure sustainable growth.
- Space Debris and Traffic Management concerns are rising as more satellites are deployed, increasing the risk of orbital congestion and collisions.
- Regulatory and Policy Frameworks must evolve to support international cooperation in space traffic management, cybersecurity, and resource utilisation.
- Economic Sustainability remains a consideration, as commercial space ventures must balance profitability with long-term operational feasibility.
- Environmental Impact is becoming a greater focus as companies work to address concerns related to rocket emissions, space debris mitigation, and sustainability.
As the space industry grows, a strong digital presence is essential. Securing the right domain name enhances credibility, strengthens brand identity, and ensures accessibility as space technologies become increasingly integrated into daily life.
Domain Names Highlights
Space companies favor .com domains (95 out of 120) and Exact Brand Match (EBM) domains (76), recognising their advantages in credibility, consistency, and global reach.
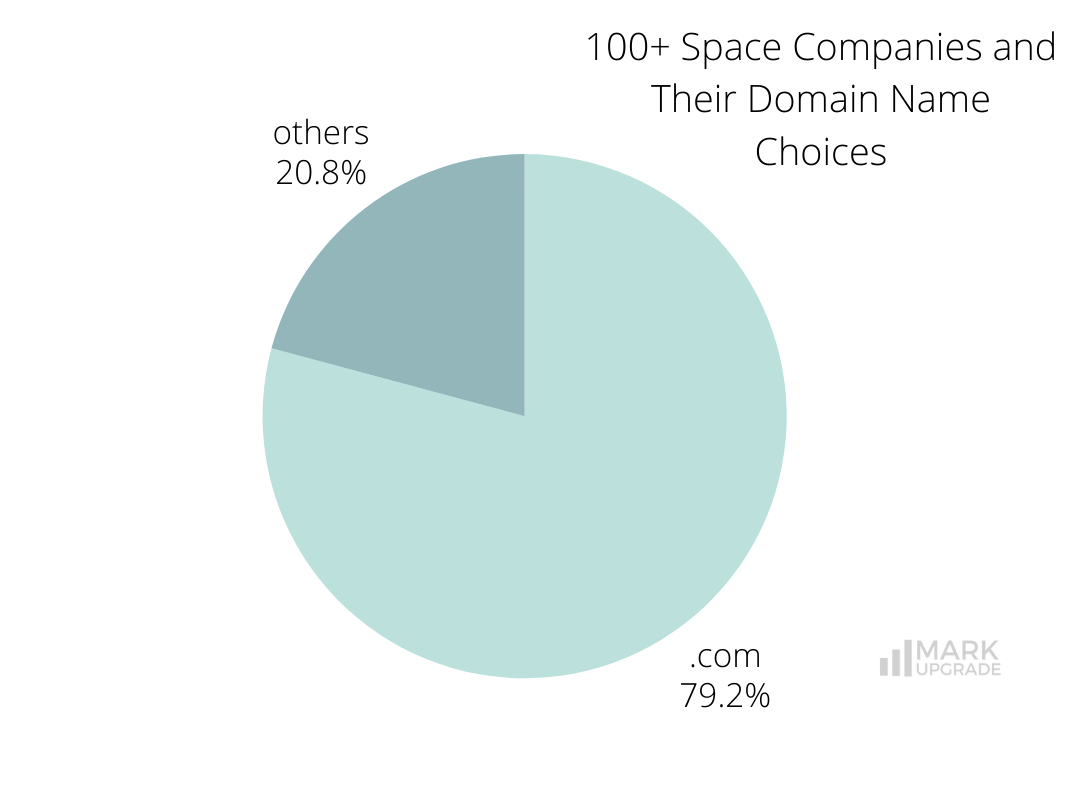
Investing in an EBM domain strengthens branding, eliminates confusion, and ensures direct web traffic flow. The .com extension enhances professionalism and trust, making it easier for customers, investors, and partners to engage with a company while supporting international expansion without regional limitations.
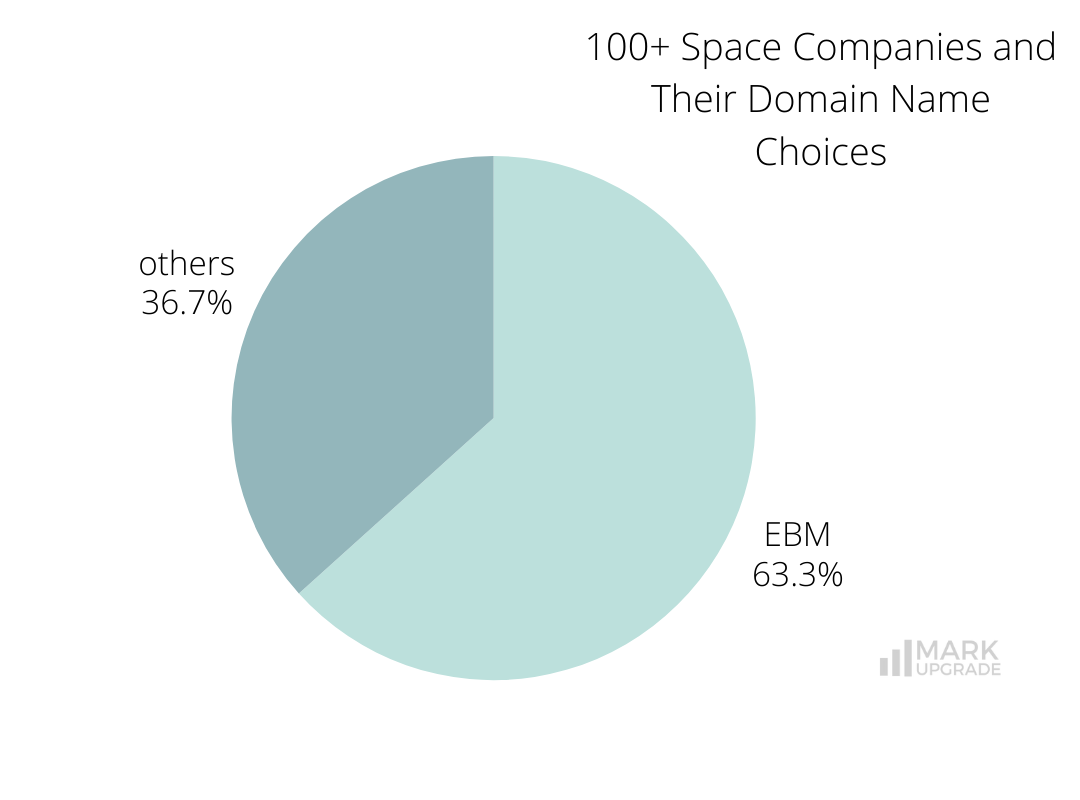
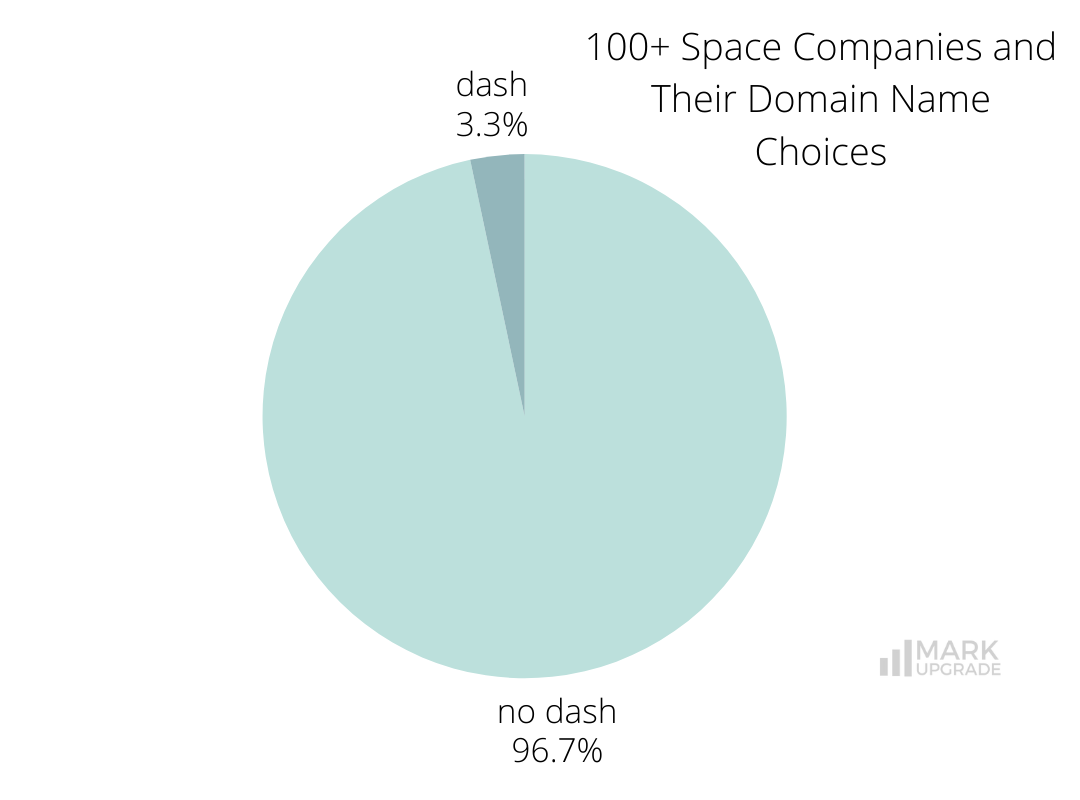
Four companies use dashes in their domains. Dashes are often included with two word brand names or with added words when the business has to compromise on their domain if the exact brand match name is taken/not within reach.
Naming Trends in Space Companies
Aerospace and Orbital References
Companies frequently use words like Aerospace, Orbital, Orbit, and Astro to highlight their connection to space technology.
Examples: Astra, Astroscale, Orbit Fab, Terran Orbital, LeoLabs.
Exploration and Discovery Themes
Names that evoke adventure, progress, and pushing boundaries reflect the spirit of space innovation.
Examples: Voyager, Exploration Company, Space Pioneer, Mission Space, Moon Express.
Tech and AI Influence
Space and AI’s intersection leads to names incorporating automation, intelligence, or futuristic elements.
Examples: a.i. solutions, Intuitive Machines, True Anomaly, and Infinite Orbits.
Short and Abstract Names
Concise, minimal names enhance memorability while suggesting technology and space.
Examples: Stoke, Varda, Vast, Mynaric, Capella Space.
Historical and Mythological Roots
Names inspired by mythology, celestial bodies, or historical figures add depth and prestige. Examples: Arianespace (Ariadne of Greek mythology), Bellatrix Aerospace (a star in Orion), Leonardo (Da Vinci), Thales Alenia Space (Greek philosopher Thales).
Namepicks
Check out our article “How to Name a Unicorn?” for insights on choosing a brand name that can help elevate your startup to unicorn status.
Arianespace
Arianespace SA, a French company founded in 1980, is the world’s first commercial launch service provider and a subsidiary of ArianeGroup, a joint venture between Airbus and Safran. The company is responsible for marketing and managing launch services for the Ariane 6 and Vega C rockets, which cater to medium-to-heavy and small-lift payloads, respectively. Operating from the Guiana Space Centre in French Guiana, Arianespace oversees mission preparation and customer relations while collaborating with government agencies and private partners to maintain Europe’s independent access to space.
With a legacy of over 850 satellite launches, Arianespace has played a key role in advancing global space capabilities.
The first commercial flight of Ariane 6 successfully launched the CSO-3 Earth observation satellite for the French Defense Procurement Agency (DGA) and CNES. This mission, completed on March 6, 2025, secured Europe’s independent access to space and completed the CSO satellite system for defense and security operations.
Interesting Fact: The name Ariane comes from the French spelling of Ariadne, a figure from Greek mythology. France initiated the Ariane project, which was officially agreed upon in 1973 as a joint effort between France, Germany, and the UK. The project, known as L3S (Lanceur de Substitution de Troisième génération or Third-Generation Substitution Launcher), was Europe’s second attempt at developing an independent launch vehicle after the unsuccessful Europa project.
The European Space Agency (ESA) assigned Aérospatiale—now part of Airbus—the task of developing the Ariane launchers, while Arianespace was established in 1980 to handle production, operations, and commercial launches. Over time, Airbus and Safran formed ArianeGroup, which now oversees the development and manufacturing of Ariane rockets, while Arianespace continues to manage launch services from the Guiana Space Centre in Kourou, French Guiana.
Arianespace operates on its Exact Brand Match (EBM) domain, Arianespace.com, ensuring strong brand identity, credibility, and seamless global accessibility.

Astroscale
Astroscale is a space technology company dedicated to space sustainability and on-orbit servicing across multiple orbital paths. The company focuses on creating solutions for managing the increasing congestion of satellites and debris in Earth’s orbits, ensuring safe and sustainable satellite operations.
Astroscale provides flexible solutions that help operators and launchers adapt to changing orbital conditions. As satellite numbers continue to grow, the company plays a key role in keeping orbits safe and accessible for the global space economy.
Interesting Fact: In 2021, Astroscale launched ELSA-d (End-of-Life Services by Astroscale-demonstration), the world’s first commercial debris removal demonstration mission. The mission successfully tested the ability to capture and remove space debris using magnetic docking technology, marking a significant step toward sustainable space operations.
As a global leader in space sustainability, Astroscale operates on its Exact Brand Match domain, Astroscale.com, solidifying its presence in the industry while ensuring seamless access for international partners, customers, and policymakers shaping the future of orbital management.
Blue Origin
Blue Origin is widely recognised for space tourism and high-profile rivalries with SpaceX and Virgin Galactic, but its deeper impact lies in advancing space exploration. The company is actively working on lunar infrastructure, with NASA contracts supporting its lunar lander and the development of Blue Alchemist, a groundbreaking technology that turns lunar regolith into solar panels. This innovation, unveiled in February 2023, has the potential to power future lunar cities, accelerating efforts toward long-term space colonisation.
It’s this generation’s job to build a road to space, so that future generations can unleash their creativity.
Jeff Bezos
Beyond lunar projects, Blue Origin recently resumed its space tourism missions with a milestone flight. On May 19, 2024, the company launched a six-person crew aboard its New Shepard rocket, including Ed Dwight, the first Black astronaut candidate from the 1960s. At 90 years and eight months, Dwight became the oldest person in space, stepping out of the capsule in celebration after the successful mission.
Interesting Fact: Blue Origin has now flown 37 private astronauts, including William Shatner, who traveled to space in 2021 at the age of 90 years and six months.
Blue Origin operates on BlueOrigin.com, an Exact Brand Match (EBM) domain that aligns with its global ambitions and strengthens its online presence. A clear and direct domain name enhances visibility, builds trust, and supports long-term brand recognition.
Eutelsat
Eutelsat S.A. is a French satellite operator providing extensive coverage across Europe, the Middle East, Africa, Asia, and the Americas. It is one of the world’s largest satellite operators, offering services for broadcasting, telecommunications, broadband, and government applications. Following its merger with OneWeb in 2023, the company now operates a fleet of 35 geostationary satellites and 600 low-Earth-orbit satellites.
Originally established as the European Telecommunications Satellite Organization (Eutelsat) in 1977 by 17 European countries, it began as an intergovernmental organisation (IGO) tasked with developing and operating a satellite-based telecommunications infrastructure for Europe.
Eutelsat facilitates the transmission of nearly 7,000 television channels and 1,100 radio stations, reaching over 274 million homes. It also provides connectivity solutions for maritime, aviation, and remote areas, strengthening global communications.
Interesting Facts: Eutelsat was the first satellite operator in Europe to offer direct-to-home television broadcasting, playing a key role in expanding satellite TV access across the continent. As of March 2025, the company announced that it offers the same capacities as Starlink in Europe, positioning itself as a direct competitor in the satellite broadband market.
Eutelsat operates on its Exact Brand Match (EBM) domain, Eutelsat.com, ensuring an accessible and easily recognisable online presence that aligns with its global communications mission.
Maxar
Founded initially as MDA in 1969, the company rebranded as Maxar in 2017 after acquiring DigitalGlobe. Specialising in satellite technology and geospatial intelligence, Maxar provides high-resolution imagery, 3D mapping, and advanced space-based solutions for defense, government, and commercial applications. Its WorldView Legion satellites enhance Earth observation, supporting national security, environmental monitoring, and urban development.
Beyond imaging, Maxar develops spacecraft platforms and robotic systems, delivering precise geospatial data and real-time intelligence to industries that rely on accurate Earth observation.
Interesting Fact: Maxar supplies 90% of the foundational geospatial intelligence used by the U.S. government, playing a critical role in national security and military operations.
Maxar has secured Maxar.com for its brand presence online. An exact brand match .com name like Maxar.com is the natural choice of most internet users, making their marketing most effective across all channels.
Orbit Fab
Orbit Fab is pioneering in-orbit refueling, branding its services as “Gas Stations in Space™.” The company develops technology that allows spacecraft to refuel while in orbit, extending their operational lifespan and improving mission efficiency. Its RAFTI™ refueling interface is designed to become the industry standard, offering a seamless docking and fuel transfer solution for satellites and spacecraft.
With plans to begin hydrazine fuel delivery by 2025, Orbit Fab is working with commercial operators and government agencies, including the U.S. Space Force and Astroscale. In addition to refueling hardware, the company provides mission planning software, UMPIRE, which optimises fuel logistics and enhances space operations.
Interesting Fact: In 2021, Orbit Fab launched the first-ever orbital fuel depot, laying the foundation for a commercial in-space refueling network. The company plans to charge $20 million for up to 100 kilograms of hydrazine, a crucial fuel for satellites.
Orbit Fab has a domain name exactly matching their brand name – Orbit Fab.com. The majority of successful global brands operate on similar names that communicate trust and authority.
SpaceX
SpaceX, officially known as Space Exploration Technologies Corp., is a pioneering private aerospace company focused on reducing the cost of space travel and advancing human exploration beyond Earth. Founded by Elon Musk in 2001, the company is at the forefront of innovation, developing reusable rocket technology and spacecraft designed to make space more accessible. SpaceX has made history with achievements like the Falcon 9 and Falcon Heavy rockets, the Dragon spacecraft, and the ongoing development of Starship—a fully reusable vehicle capable of deep-space missions.
Beyond exploration, SpaceX is also shaping global connectivity through Starlink, a satellite constellation delivering high-speed internet to underserved regions worldwide. The company’s breakthroughs have transformed the commercial space industry, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in space travel and technology.
Interesting Fact: In 2024, SpaceX’s Polaris Dawn mission made history by conducting the first-ever private spacewalk and reaching the highest Earth orbit since the Apollo era. This milestone further demonstrated the potential of commercial spaceflight and reinforced SpaceX’s commitment to expanding human presence in space.
Elon Musk’s focus on strong digital branding is evident in SpaceX’s use of the Exact Brand Match domain SpaceX.com, reinforcing global recognition and ensuring a seamless online presence.

The right domain name is an important consideration when it comes to building and protecting your brand. If you’re ready to take the next step and invest in a perfect domain name for your business, contact us to learn more about our available options and how we can help you get started.
Other resources
branding business domain domain name domain names domains naming Space companies

Previous Next